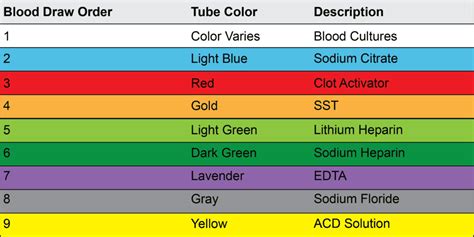
Phlebotomy, the process of collecting blood samples for laboratory testing, requires a high degree of precision and attention to detail to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the test results. One critical aspect of phlebotomy is the order of draw, which refers to the sequence in which different tubes are filled with blood during a single venipuncture procedure. The order of draw is crucial because it helps prevent cross-contamination of additives between tubes, which can lead to inaccurate test results or even render the sample unusable.
The order of draw was first established by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) in the 1980s and has since been widely adopted as a standard practice in the medical field. The recommended order of draw is as follows: blood culture bottles, coagulation tubes (e.g., sodium citrate), serum separator tubes (SST) or serum tubes with clot activator and gel, heparin tubes (e.g., plasma separator tubes, PST), EDTA tubes (e.g., lavender top), and finally, glycolytic inhibitor tubes (e.g., gray top). This order is designed to minimize the risk of contamination and ensure that each tube is filled with the correct type and amount of blood.
Key Points
- The order of draw in phlebotomy is a critical aspect of the blood collection process, as it helps prevent cross-contamination of additives between tubes.
- The recommended order of draw is: blood culture bottles, coagulation tubes, serum separator tubes, heparin tubes, EDTA tubes, and glycolytic inhibitor tubes.
- The order of draw is designed to minimize the risk of contamination and ensure that each tube is filled with the correct type and amount of blood.
- Following the correct order of draw is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of laboratory test results.
- Phlebotomists should always follow the recommended order of draw and use the correct type of tube for each test to prevent errors and ensure patient safety.
Importance of Order of Draw in Phlebotomy
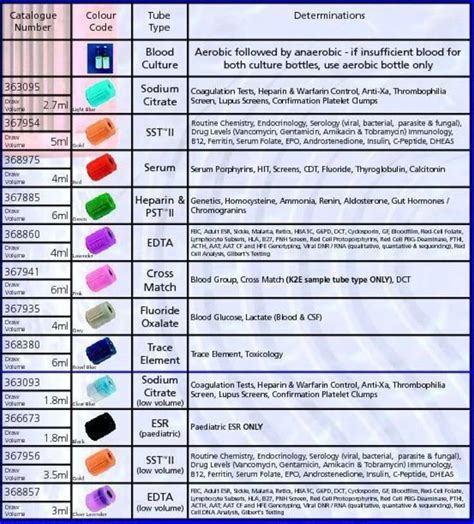
The importance of the order of draw cannot be overstated, as it plays a critical role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of laboratory test results. If the wrong tube is filled first, or if the tubes are filled in the wrong order, it can lead to cross-contamination of additives, which can affect the test results. For example, if a coagulation tube is filled after an EDTA tube, the EDTA can contaminate the coagulation tube and affect the coagulation test results.
In addition to preventing cross-contamination, the order of draw also helps to ensure that each tube is filled with the correct type and amount of blood. For example, blood culture bottles require a specific amount of blood to be effective, and filling them first ensures that the correct amount is collected. Similarly, coagulation tubes require a specific ratio of blood to anticoagulant, and filling them after the blood culture bottles helps to ensure that this ratio is maintained.
Common Mistakes in Order of Draw
Despite the importance of the order of draw, mistakes can still occur. Common mistakes include filling the tubes in the wrong order, using the wrong type of tube for a particular test, or failing to fill the tubes to the correct level. These mistakes can lead to inaccurate test results, which can have serious consequences for patient care.
To avoid these mistakes, phlebotomists should always follow the recommended order of draw and use the correct type of tube for each test. They should also ensure that the tubes are filled to the correct level and that the blood is properly mixed with the additives. By following these guidelines, phlebotomists can help ensure the accuracy and reliability of laboratory test results and provide high-quality care to patients.
| Tube Type | Additive | Order of Draw |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Culture Bottle | None | 1 |
| Coagulation Tube | Sodium Citrate | 2 |
| Serum Separator Tube (SST) | Clot Activator and Gel | 3 |
| Heparin Tube | Lithium Heparin | 4 |
| EDTA Tube | EDTA | 5 |
| Glycolytic Inhibitor Tube | Fluoride and Oxalate | 6 |

Best Practices for Order of Draw
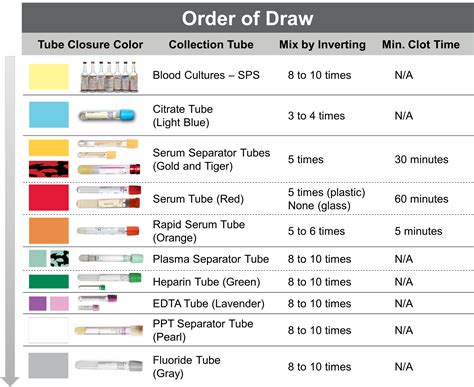
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of laboratory test results, phlebotomists should follow best practices for order of draw. These include:
1. Always follow the recommended order of draw: The order of draw should be followed in the correct sequence to prevent cross-contamination of additives and ensure that each tube is filled with the correct type and amount of blood.
2. Use the correct type of tube for each test: Different tests require different types of tubes, and using the wrong type of tube can affect the test results. Phlebotomists should always use the correct type of tube for each test.
3. Fill the tubes to the correct level: Filling the tubes to the correct level is essential to ensure that the correct amount of blood is collected and that the additives are properly mixed with the blood.
4. Properly mix the blood with the additives: After filling the tubes, phlebotomists should properly mix the blood with the additives to ensure that the additives are evenly distributed throughout the blood.
5. Label the tubes correctly: Labeling the tubes correctly is essential to ensure that the tubes are properly identified and that the test results are matched to the correct patient.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the order of draw is a critical aspect of phlebotomy, and following the recommended order of draw is essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of laboratory test results. By following best practices for order of draw, phlebotomists can help ensure that each tube is filled with the correct type and amount of blood, and that the additives are properly mixed with the blood. This, in turn, helps to ensure that laboratory test results are accurate and reliable, which is essential for providing high-quality care to patients.
What is the recommended order of draw in phlebotomy?
+The recommended order of draw is: blood culture bottles, coagulation tubes, serum separator tubes, heparin tubes, EDTA tubes, and glycolytic inhibitor tubes.
Why is the order of draw important in phlebotomy?
+The order of draw is important because it helps prevent cross-contamination of additives between tubes, which can affect the accuracy and reliability of laboratory test results.
What are the consequences of not following the recommended order of draw?
+The consequences of not following the recommended order of draw include inaccurate test results, which can have serious consequences for patient care.