Cement curing time is a critical factor in the construction industry, as it directly affects the strength, durability, and overall quality of concrete structures. The curing process involves maintaining a consistent level of moisture and temperature to facilitate the chemical reaction between cement and water, ultimately leading to the formation of a solid and stable matrix. With the increasing demand for sustainable and efficient construction practices, understanding the intricacies of cement curing time has become essential for engineers, architects, and builders.
Historically, the concept of cement curing dates back to the early 19th century, when French engineer Louis Vicat discovered that cement could be improved by adding water and allowing it to set. Since then, significant advancements have been made in understanding the curing process, including the development of new cement types, such as rapid-hardening cement and low-heat cement. These advancements have enabled the construction of complex structures, including high-rise buildings, bridges, and dams, with enhanced durability and reduced maintenance requirements.
Key Points
- Cement curing time is influenced by factors such as temperature, humidity, and cement type
- The ideal curing temperature for most cement types is between 20°C and 25°C
- Rapid-hardening cement can achieve significant strength in as little as 24 hours, while low-heat cement may take up to 28 days
- Adequate curing can increase concrete strength by up to 30%
- Insufficient curing can lead to reduced durability, increased maintenance costs, and potential structural failures
Cement Curing Process

The cement curing process involves a series of complex chemical reactions, which can be broadly categorized into four stages: hydration, setting, hardening, and maturity. During the hydration stage, cement particles react with water to form a gel-like substance, which gradually solidifies as the curing process progresses. The setting stage marks the transition from a fluid to a solid state, while the hardening stage is characterized by a significant increase in strength and durability. Finally, the maturity stage represents the point at which the concrete has reached its maximum strength and stability.
Curing Methods and Techniques
Various curing methods and techniques are employed to ensure optimal cement curing, including water curing, steam curing, and membrane curing. Water curing involves applying a layer of water to the concrete surface, while steam curing uses a controlled environment to accelerate the curing process. Membrane curing, on the other hand, involves applying a impermeable membrane to prevent moisture loss and promote uniform curing. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of curing technique depends on factors such as climate, cement type, and project requirements.
| Cement Type | Curing Time | Compressive Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid-hardening cement | 24 hours | 20 MPa |
| Low-heat cement | 28 days | 30 MPa |
| Ordinary Portland cement | 7 days | 25 MPa |

Factors Influencing Cement Curing Time
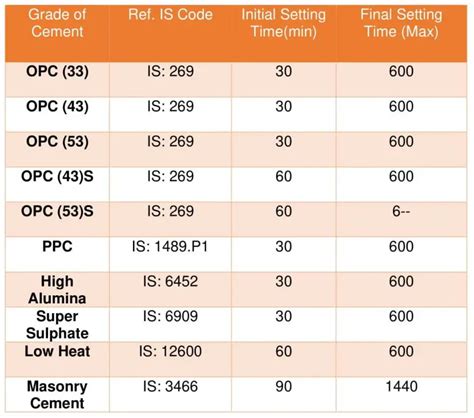
A range of factors can influence cement curing time, including temperature, humidity, cement type, and mix design. Temperature, in particular, plays a critical role, as it can accelerate or decelerate the curing process. Generally, the ideal curing temperature for most cement types is between 20°C and 25°C. Humidity, on the other hand, affects the rate of moisture loss, which can impact the curing process. Cement type and mix design also significantly influence curing time, as different types of cement and aggregate combinations can exhibit varying rates of hydration and hardening.
Consequences of Insufficient Curing
Insufficient curing can have severe consequences, including reduced durability, increased maintenance costs, and potential structural failures. When concrete is not properly cured, it can lead to a range of problems, such as cracking, scaling, and spalling. Furthermore, inadequate curing can compromise the structural integrity of the concrete, leading to a reduced lifespan and increased risk of failure. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that concrete is properly cured to achieve optimal strength, durability, and performance.
What is the ideal curing temperature for most cement types?
+The ideal curing temperature for most cement types is between 20°C and 25°C.
What are the consequences of insufficient curing?
+Insufficient curing can lead to reduced durability, increased maintenance costs, and potential structural failures.
How does cement type affect curing time?
+Cement type can significantly influence curing time, as different types of cement exhibit varying rates of hydration and hardening.
In conclusion, cement curing time is a critical factor in the construction industry, and understanding its intricacies is essential for achieving optimal strength, durability, and performance. By recognizing the factors that influence curing time and employing suitable curing methods and techniques, construction professionals can ensure that their projects meet the highest standards of quality and sustainability. As the construction industry continues to evolve, the importance of cement curing time will only continue to grow, making it essential for professionals to stay up-to-date with the latest advancements and best practices in this field.



